If you’ve ever shopped for a new bike, you’ve probably heard the term “bike geometry.” But what does that even mean? Are we going back to a high school math class? Let’s take a closer look at this term and see if it reminds you of the polygon study. But first—what is bike geometry?
In this post, you will learn the basics of bike geometry and some terms and definitions every cyclist should know.
Bike geometry is a collection of measurements in lengths and angles that define a bike’s configuration. These measurements play a critical role in how a bike performs.
Before knowing how geometry affects your bike, let’s first understand what bike geometry is.
What is bike geometry?

Bike geometry is a collection of measurements in lengths and angles that define a bike’s configuration. The key focus areas are the wheelbase, steering axis angle, fork offset, and trail. These measurements all play a significant role in how a bike handles.

State Bicycle Co. Black Label 6061

State Bicycle Co. Black Label 6061
How does geometry affect a bike?
A bike’s geometry influences its performance in several ways, depending on its design and manufacture. When constructing a bike, it is critical to consider the rider’s weight and size. Different bikes are built for different types of riders. The geometry of the bike influences how it handles and rides. A bike with a larger frame, for example, will ride more stably and smoothly than one with a smaller frame.
How do you find the geometry on a bike?
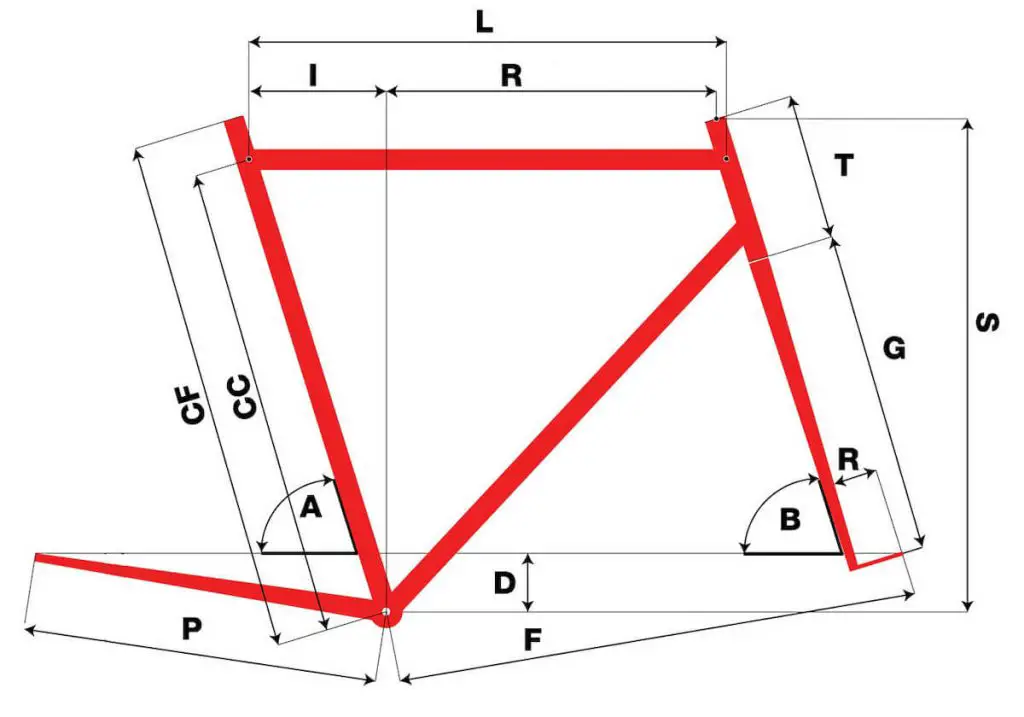
Since geometry varies based on the bike, there are a few things you may do to determine a bike’s geometry:
- Search for the bike online. The manufacturer should have some information online about the geometry of the bike.
- Examine the frame: The frame is generally the most obvious portion of a bike and will indicate the bike’s form and size. Look for a sticker that provides more information.
- Inspect the frame, stem, and seat. These bike components can also provide information on the bike’s geometry.
What is a good bike geometry?
The optimal geometry for a bike varies based on your height, weight, riding style, and other factors. However, here are some general guidelines to help you select the best geometry for your requirements:
- Test out various bikes to find one that is comfortable and matches your riding style.
- Bigger riders sometimes require a heavier bike to keep steady. Test out several bikes until you get one that is a good match for your physique.
- Find a bike that matches your height. The taller you are, the higher you must ride to stay upright. Test out several bikes until you discover one that matches your height well.
Basic bicycle geometry terminology
When we talk about bike geometry, you should consider the following terms. Each of these has an impact on the feel of your bike. Therefore, you may want to adjust and customize these to fit your needs.
1 . Frame size
This is one of the most significant parts of a bike’s anatomy. The frame is what everything else is based upon. Without the frame, there is no bike.
The bike size is usually measured from where the seat post starts to the crank, measured in centimeters. However, you might occasionally find a manufacturer that refers to their bikes as small, medium, or large. Double-check what that size means to that manufacturer to avoid confusion.
If you want some help in determining your ideal frame size, check out our guide on how to choose a fixed-gear bike. You can also check out the simple breakdown of frame sizes and how they relate to a human’s height below. This is an excerpt from a post on bicycleguider.com. Their full guide on bike frames can be found here.
| Rider height | Leg inseam | Frame | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feet/Inches | Centimeters | Inches | Centimeters | Inches | Size |
| 4’10”-5’1″ | 147-155 cm | 24-29″ | 61-73 cm | 14″ | XS |
| 5’1′-5’5′ | 155-165 cm | 25-30″ | 63-76 cm | 15″ | S |
| 5’5′-5’9′ | 165-175 cm | 26-31″ | 66-78 cm | 16″ | M |
| 5’9′-6’0′ | 175-183 cm | 27`-32` | 68-81 cm | 17″ | L |
| 6’0′-6’3′ | 183-191 cm | 28`-33` | 71-83 cm | 18″ | XL |
| 6’1′-6’6′ | 191-198 cm | 29`-34` | 73-86 cm | 19″ | XXL |
2. Stack
The stack refers to the vertical portion of the bike when measured from the center of the frame up to the top of the head tube. This helps determine how tall a frame is.
3. Reach
The reach refers to the horizontal measurement of the frame from the center of the bottom bracket to the top center of the head tube. This helps determine how long the time frame is.
If a bike is too tall or long for an individual, they won’t be able to ride it comfortably, and they should find a bike with shorter dimensions of these metrics.
To determine your stack and reach measurements, check out our guide on calculating your bike’s stack and reach.
4. Head tube
The head tube angle deals with the direction of the head tube relative to the ground. The standard head tube is at a 73-degree angle on a road bike. The steeper (or higher) the number, the less difficult the bike is to steer. And the bike will also be more agile.
5. Fork rake
The fork rake (the offset) is the distance between the steering axis and the wheel center.
6. Trail
The trail is best described as the tire patch behind the steering axis. Its size is determined by the head tube angle and fork rake. A smaller trail means a bike with better handling. A bike with a lot of trails is going to be better for high speeds.
As you can see from the image below, the trail can get very complicated very fast.
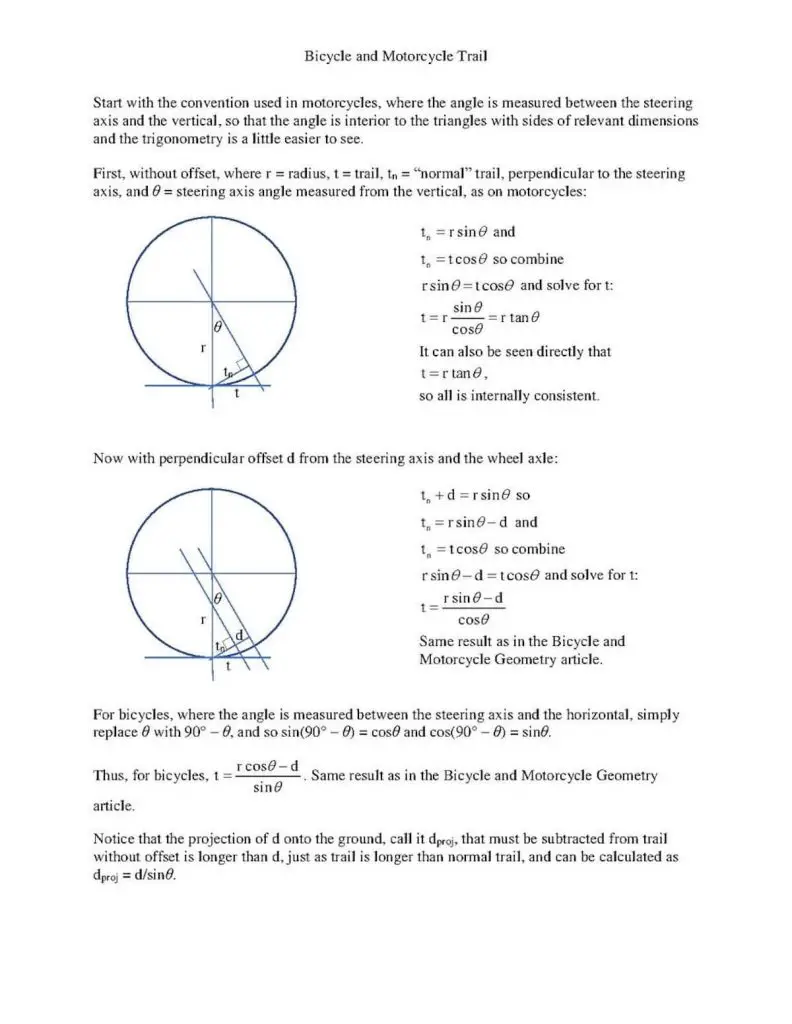
The whole thing involves a lot of math. But you don’t have to go through and be a rocket surgeon to figure this stuff out. Nowadays, you can just check out this nifty online trail calculator!
7. Drop of the Bottom Bracket
This measurement comes from how far the bottom bracket sits below the wheel axis. This measurement translates into how low you sit on the bike. It’s something to be aware of if you want or need to be elevated on your bike.
And the lower this number, the faster the bike will respond to changes in speed and steering. The average drop averages out to about seven centimeters. If the drop gets much lower, it can be challenging to pedal around corners.
8. Seat Tube & Seat Tube Angle
The seat tube angle refers to the angle of the seat tube with the ground. If you change the seat tube angle, you can alter how steep or “slack” the bike is in the saddle position. This angle tends to stay between 71 and 74 degrees. The seat tube is the portion of the bike that holds the seat or saddle.
9. Chain-stay Length
You can get this measurement by taking the horizontal distance from the bottom bracket to the center of the rear axle.
The length of the chainstay impacts the length of the wheelbase and how the bike handles overall. The longer the chainstay, the more stable the bike is. This design works well on an endurance bike. However, shorter chainstays work better on performance bikes and allow for sharper handling.
Check out the products below if you’re in the market for a new chain.
[azonpress template=”grid” asin=”B001CNARIE,B07NRD3QBF,B00H2H4TII”]
10. Wheelbase
The wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the two wheels of a bike. It is measured by determining the distance between the centers of the two wheels. A long wheelbase is ideal for high speeds. The front center isn’t as crucial as other bike measurements. It is more of a nice-to-know measurement. This measurement can help judge the overlap between bikes.
11. Weight distribution
Make sure your weight is distributed correctly on a bike. Under ideal circumstances, 45% of a bike’s and rider’s weight should be distributed on the front wheel. The remaining 55% should be on the back wheel. You can check this on any type of scale.
Proper weight distribution is crucial for optimal performance. Too much weight on either wheel makes it difficult for a bike to turn and/or climb.
12. Standover height
The standover height is the distance between the ground and the top tube of the bike. This is one of the most important measurements to consider when purchasing a bike.
Below is a video on determining your standover height from Pure Cycles called “Bike Sizing: Laying down the law on how to properly size yourself up on a fixed gear bike”
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Below are some commonly asked questions regarding bike geometry.
What difference does bike geometry make?
The geometry of a bike impacts two critical aspects: how the bike handles and your position on it.
Does bike geometry affect speed?
An aerodynamic frame would help cyclists ride quicker since they could create more power. Others feel that the style of bike you ride has a modest but considerable influence on your speed and that the greatest racing bikes have aero frames and shorter wheelbases.
What is a relaxed geometry bike?
A relaxed geometry bike is a type of bike that was created to assist people who suffer from back and neck problems. It is also a recumbent bike since it is meant to recline back towards the user. This allows the user to rest their head and neck more easily on the bike’s seat.
Does a 1-degree head angle make a difference?
Some people may notice a substantial difference in their riding experience with a 1-degree head angle, while others may not notice any difference at all. Many riders, however, think that a 1-degree head angle gives a smoother ride since it lowers the length of trail your front wheel rolls on. However, it is crucial to remember that a 1-degree head angle is not the only aspect that influences how a bike rides.
What is a good BB height?
According to standard guidelines, an individual’s BB height should be between 18 and 22 inches. So, you’re in good shape if you’re between these heights!
What does slack geometry mean on a bike?
It is a technique for reducing aerodynamic drag on a bicycle. It’s most typically employed while riding in a drafting position behind another rider since the draft pushes the cyclist in front’s front wheel down and away from the wind. This results in less air resistance on the front tire, allowing you to ride faster.
Is stack or reach more important?
A higher stack for a given reach puts you in a more upright riding position; your hands will be moved upwards, and your body position will be more vertical.
If you keep the stack the same but increase the reach, you’ll have a longer riding posture; your hands will go forward, and you’ll be more spread out.
You can fine-tune your ride position by changing your stem, adding or removing headset spacers, and so on, but only so much, which is why stack and reach are so crucial to a bike.
What is a trail in bike geometry?
The length of the ground between the contact points of the front and rear wheels is referred to as the trail in bike geometry. The trail is essential in bicycle design because it influences how the bicycle performs when ridden. For example, at high speeds, a bike with more trails will feel more stable and responsive, whereas a bike with little trail will be more agile and simpler to maneuver.
Conclusion
This is a lot of information, especially if you aren’t familiar with any of these terms. To find your ideal geometry, take a few bikes for a spin, and note the one you like best. There is no better way to know what kind of bike feels best for you than to give it a spin. Then, have the shop provide you with info on that bike’s measurements.
We hope this post taught you some bike geometry terminology you can use next time you need to upgrade or adjust your bike.
This article covered the basics of bike geometry and provided some of the definitions you should know. Here are some key takeaways:
Key takeaways
- Bike geometry refers to the angles on a bike’s frame and fork.
- Finding your perfect measurements can help you pick the perfect bike for you.
- To find your ideal geometry, take a few bikes for a spin and note the one you like best; then, have the shop provide you with info on that bike’s measurements.
So, have you ever heard of bike geometry? Is there anything you’d like to add to this post? Let us know in the comments below (we read and reply to every comment). If you found this article helpful, check out our full blog for more tips and tricks on everything fixie. Thanks for reading, and stay fixed.
Helpful resources
- Articles about fixed gear and single-speed cycling and equipment
- A hipster’s guide to bike geometry. | Fixie bike, Fixie, bicycle
- Speed Vs. Stability-GCN at The Bicycle Academy
- Fixed-gear bicycle – Wikipedia
















